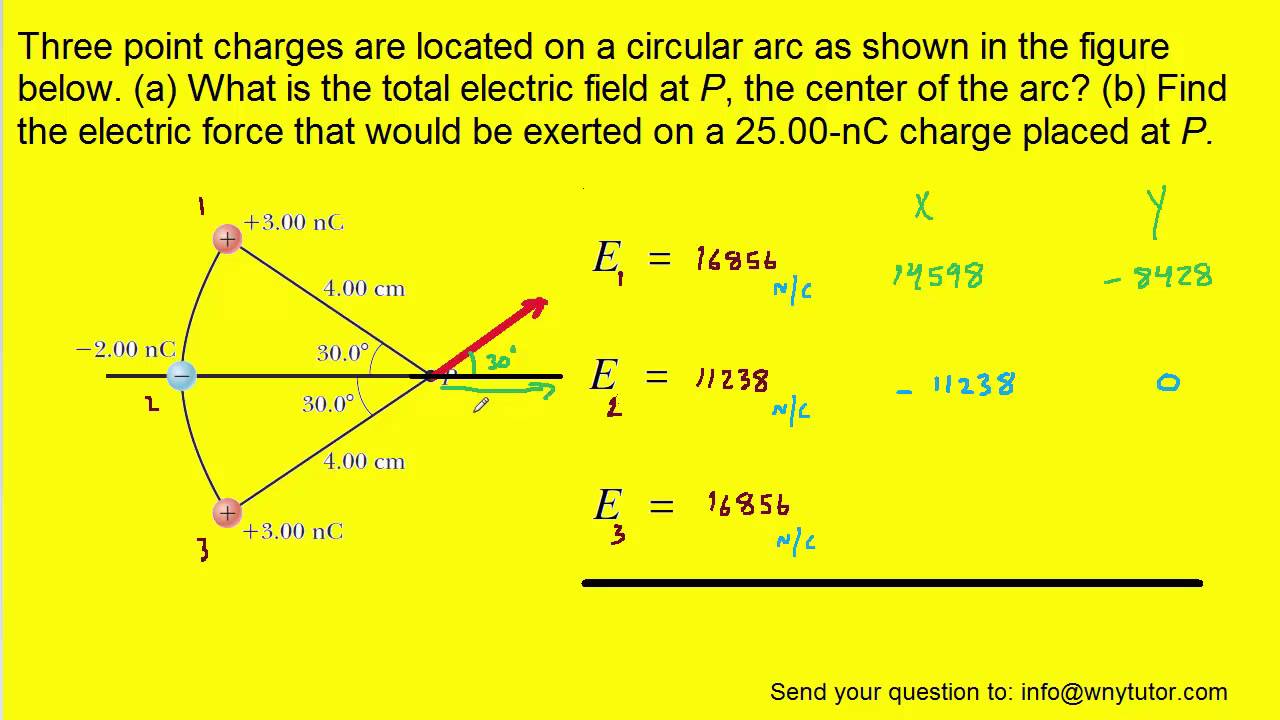
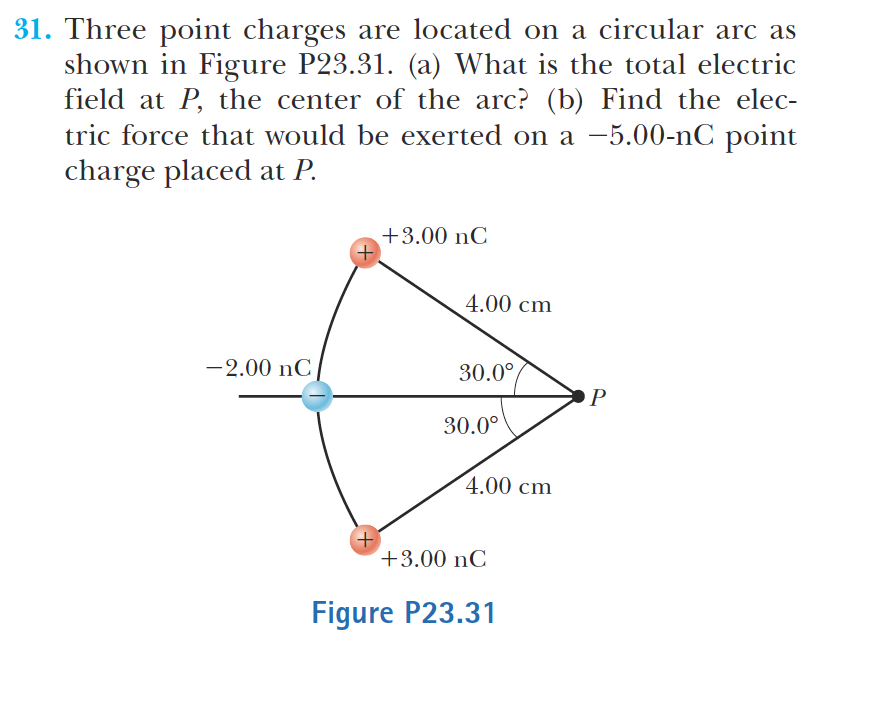
Three-point charge problems, specifically those arranged on a circular arc, offer a great opportunity to explore Coulomb's Law and vector addition. Let's dive in!
Understanding the Setup
The basic scenario involves three electric charges. These are placed at specific locations along a circular arc. We want to determine the net electric force on a specific charge.
Students need a clear understanding of the problem. The geometry of the circular arc is important. They must know the angles and distances involved.
Tips for Educators:
Begin with simple examples. Equal charges and symmetrical arrangements work well. This helps to build intuition. Gradually increase the complexity. Introduce unequal charges and asymmetrical positions.
Use diagrams. These help to visualize the forces involved. Ensure the charges, distances, and angles are clearly labeled. Encourage students to draw their own diagrams.
Review basic trigonometry. Sine, cosine, and tangent are essential for resolving force vectors. Make sure students are comfortable with these concepts. This is often a stumbling block.
Applying Coulomb's Law
Coulomb's Law quantifies the electric force. It acts between two point charges. The formula is F = k * q1 * q2 / r^2. k is Coulomb's constant. q1 and q2 are the magnitudes of the charges. r is the distance between them.
We calculate the force. Do this between each pair of charges. Focus on the charge experiencing the net force. Determine the magnitude of each individual force.
Remember the direction. The force is attractive if the charges have opposite signs. The force is repulsive if the charges have the same sign. Indicate the direction of the force on the diagram.
Tips for Educators:
Emphasize the importance of units. Ensure students are using consistent units. Coulombs for charge and meters for distance are crucial. This will prevent errors in calculations.
Discuss the concept of superposition. The net force is the vector sum of individual forces. Each charge contributes independently to the total force. This is a fundamental principle.
Provide practice problems. Start with simpler cases. Work up to more challenging scenarios. This helps to solidify understanding.
Vector Addition
Electric force is a vector. It has both magnitude and direction. Therefore, we must use vector addition. We will determine the net force.
Resolve each force into components. Typically, these are x and y components. Use trigonometry to find these components. Sum the components in each direction.
Calculate the magnitude of the net force. Use the Pythagorean theorem. The magnitude is sqrt(Fx^2 + Fy^2). Determine the direction of the net force. Use the inverse tangent function. The direction is arctan(Fy/Fx).
Tips for Educators:
Review vector components. Students should understand how to break down a vector. Emphasize the importance of correct signs. These are critical for accurate calculations. Pay close attention to angle conventions.
Use graphical methods. Visualizing the vector addition helps. Draw a vector diagram showing the individual forces. Also draw the resultant net force.
Discuss the limitations of using arctangent. The arctangent function only gives angles in the first and fourth quadrants. Students must consider the signs of Fx and Fy. Adjust the angle accordingly.
Common Misconceptions
Many students struggle with the concept of superposition. They forget to add forces vectorially. They treat force as a scalar quantity.
Another common mistake is incorrect angle calculations. They may not use the correct angles for resolving vectors. They may use the wrong trigonometric functions. They must pay close attention to the geometry of the problem.
Students often forget to consider the signs of the charges. This leads to incorrect force directions. They may misinterpret attractive and repulsive forces.
Tips for Educators:
Address these misconceptions directly. Dedicate time to explaining the concept of superposition. Emphasize the vector nature of force. Provide plenty of examples.
Encourage students to check their work. Verify the direction and magnitude of each force. Review their angle calculations. Look for inconsistencies.
Provide feedback. Correct errors promptly. Help students understand their mistakes. Offer guidance on how to avoid these errors in the future. Encourage peer teaching.
Making it Engaging
Use simulations. These can help students visualize the forces. They can manipulate the charges and observe the resulting net force. This can make the concept more intuitive.
Incorporate real-world examples. Discuss applications of electric forces. Examples include electrostatic painting and laser printers. This helps to connect the theory to practical applications.
Assign group projects. Students can work together to solve complex problems. They can present their solutions to the class. This promotes collaboration and critical thinking.
Tips for Educators:
Use interactive simulations. PhET simulations are a great resource. These allow students to explore the concepts in a dynamic way. This provides hands-on experience.
Relate the topic to other areas of physics. Connect electrostatics to circuits and electromagnetism. Show students how these concepts are interconnected. This provides a more holistic understanding.
Encourage questions. Create a classroom environment. Encourage students to ask questions. Foster open discussion.
By addressing common misconceptions. Emphasizing the importance of vector addition. Using engaging teaching strategies. You can help your students master this challenging concept.
Remember to celebrate their success. Recognize their hard work and effort. Positive reinforcement can motivate students. It encourages continued learning.