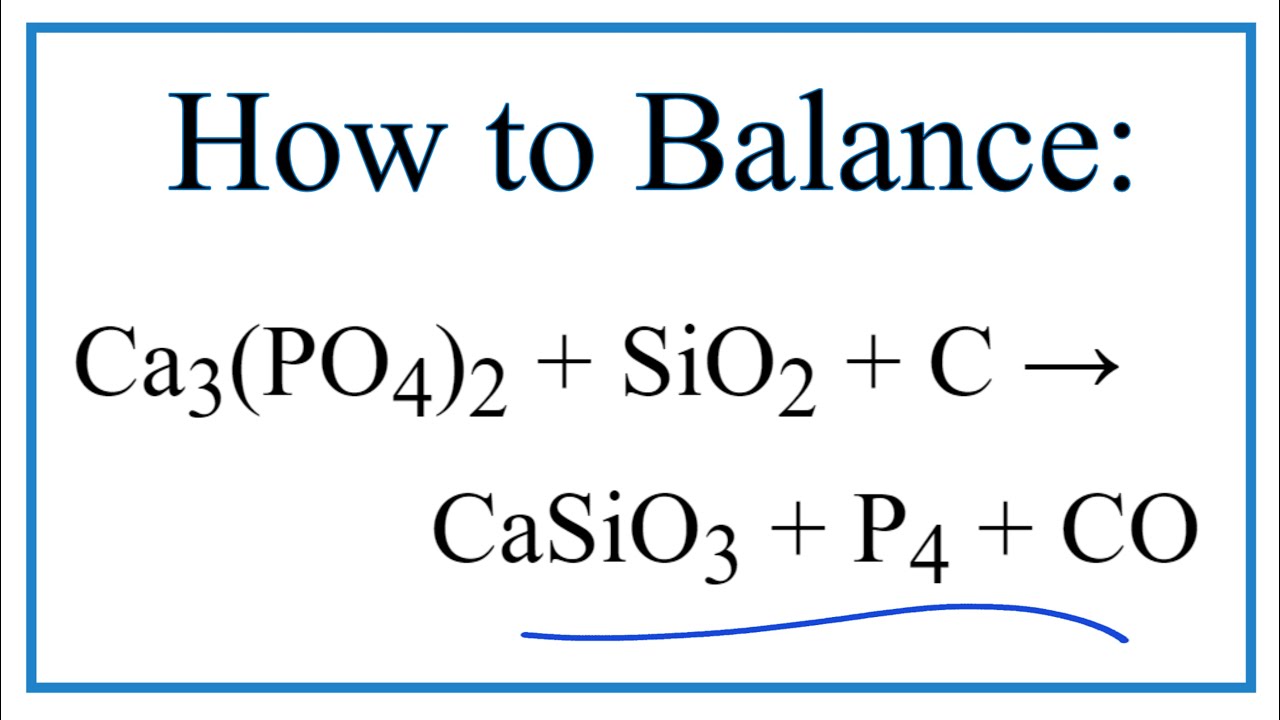
Welcome, educators! Let's explore a seemingly complex chemical mixture: Ca3(PO4)2·SiO2·C·CaSiO3·P4·CO. This can be daunting, but broken down, it presents valuable learning opportunities.
Deconstructing the Chemical Soup
First, identify each component. Ca3(PO4)2 is calcium phosphate. SiO2 is silicon dioxide (silica). C stands for carbon. CaSiO3 is calcium silicate. P4 represents tetraphosphorus. Finally, CO is carbon monoxide. Each plays a crucial role in different chemical processes and geological formations.
Calcium Phosphate (Ca3(PO4)2)
Calcium phosphate is essential. Think about bones and teeth. It's a major component of these structures. It provides rigidity and strength. It also plays a role in various biological processes.
Discuss with students where they encounter calcium phosphate. Ask about food labels. Bone health should be at the forefront of the discussion. You can even talk about potential sources of Calcium in the environment and diet.
Silicon Dioxide (SiO2)
Next, consider silicon dioxide. It's sand and quartz. It is extremely abundant in the Earth's crust. It forms the basis of many rocks and minerals. It has lots of uses in technology too.
Demonstrations with sand or quartz can be captivating. Relate it to glass production. Talk about the applications of silicon chips. This will make the connection to technology tangible for students. Explain how it's used as a raw material in various industries.
Carbon (C)
Carbon's presence is significant. It exists in many forms. Graphite and diamond are examples. It is the backbone of organic chemistry. It is also central to life itself.
Discuss allotropes of carbon. Show examples of graphite pencils and diamond jewelry. Explain the difference in structure and properties. Discuss carbon's role in combustion processes.
Calcium Silicate (CaSiO3)
Now, we have calcium silicate. It is a component of cement. It is formed in high-temperature reactions. It has important structural applications.
Discuss the formation of calcium silicate during cement production. Relate it to construction. Talk about the importance of cement in modern society. Show pictures of different cement structures.
Tetraphosphorus (P4)
Tetraphosphorus can be dangerous. It is highly reactive. It exists as white phosphorus. It ignites spontaneously in air.
Stress the dangers associated with tetraphosphorus. Emphasize that students should never handle it. Discuss its historical uses in matches and warfare. Talk about safe handling procedures in industrial settings.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Finally, we have carbon monoxide. It's a silent killer. It is a colorless, odorless gas. It is a product of incomplete combustion.
Discuss the dangers of carbon monoxide poisoning. Explain its effects on the body. Talk about carbon monoxide detectors. Emphasize the importance of proper ventilation.
Common Misconceptions
Students might think that all compounds are safe. They may misunderstand reactivity. They might not grasp the difference between elements and compounds. Address these directly. Clear explanations are key.
One common misconception is that all chemical formulas represent pure substances. Emphasize that the given formula represents a mixture of different compounds. Illustrate this concept with everyday examples of mixtures, like salad or trail mix.
Engaging Activities
Create a "chemical detective" activity. Give students clues about each compound. Have them identify the compound. Use visual aids like posters and models. Bring physical samples of materials. Safety is paramount.
Conduct a virtual lab simulation. Explore the reactions involving these compounds. Use online resources to visualize molecular structures. This can be a great way to enhance understanding. Always supervise and give clear instructions.
A scavenger hunt can be effective. Have students find examples of each compound in everyday life. This promotes engagement and real-world application. Adapt the activity to suit the available resources.
Consider a collaborative project. Have students research each compound. Ask them to present their findings. This promotes teamwork and critical thinking. Guide students to reliable information sources.
Teaching Tips
Break down complex concepts into smaller, manageable pieces. Use analogies to relate abstract concepts to real-world situations. Encourage questions and discussions. Foster a safe and supportive learning environment.
Use visuals to illustrate the concepts. Diagrams, videos, and simulations can be invaluable tools. Provide hands-on activities to reinforce learning. Make learning fun and engaging.
Relate the topic to current events. Discuss the role of these compounds in industries and research. This demonstrates the relevance of chemistry in our lives. It also shows potential career paths.
Assess student understanding through various methods. Quizzes, projects, and presentations can provide valuable feedback. Adapt teaching strategies based on student needs. Provide individualized support as needed.
Always prioritize safety. Supervise students closely during experiments. Provide clear instructions and safety guidelines. Emphasize the importance of responsible behavior in the lab. Make sure the students understand the hazards and ways to avoid them.
In summary, tackling Ca3(PO4)2·SiO2·C·CaSiO3·P4·CO can be an exciting challenge. With the right approach, you can inspire your students. You can ignite their curiosity. You can develop their critical thinking skills. This will serve them well in their future studies.