Monohybrid crosses investigate the inheritance of a single trait.
What is a Monohybrid Cross?
It is a genetic cross. It studies how one trait is passed down.
Consider pea plants. Let's examine flower color. The flowers can be purple or white.
Genotype is the genetic makeup. It describes the alleles.
Phenotype is the observable trait. It is the physical expression of the genotype.
Alleles are versions of a gene.
Homozygous means two identical alleles. Heterozygous means two different alleles.
Example: PP (homozygous dominant), pp (homozygous recessive), Pp (heterozygous).
Purple flowers (P) are dominant. White flowers (p) are recessive. This means that a plant only needs one 'P' allele to have purple flowers. Only 'pp' plants display white flowers.
Punnett Squares
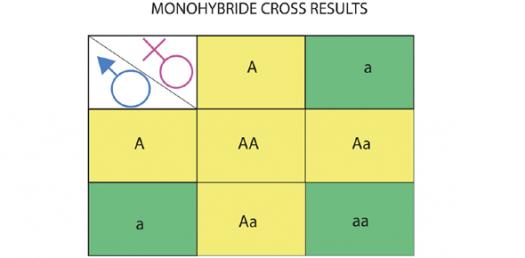
A Punnett square is a tool. It predicts the outcome of a cross.
We use it to calculate probability.
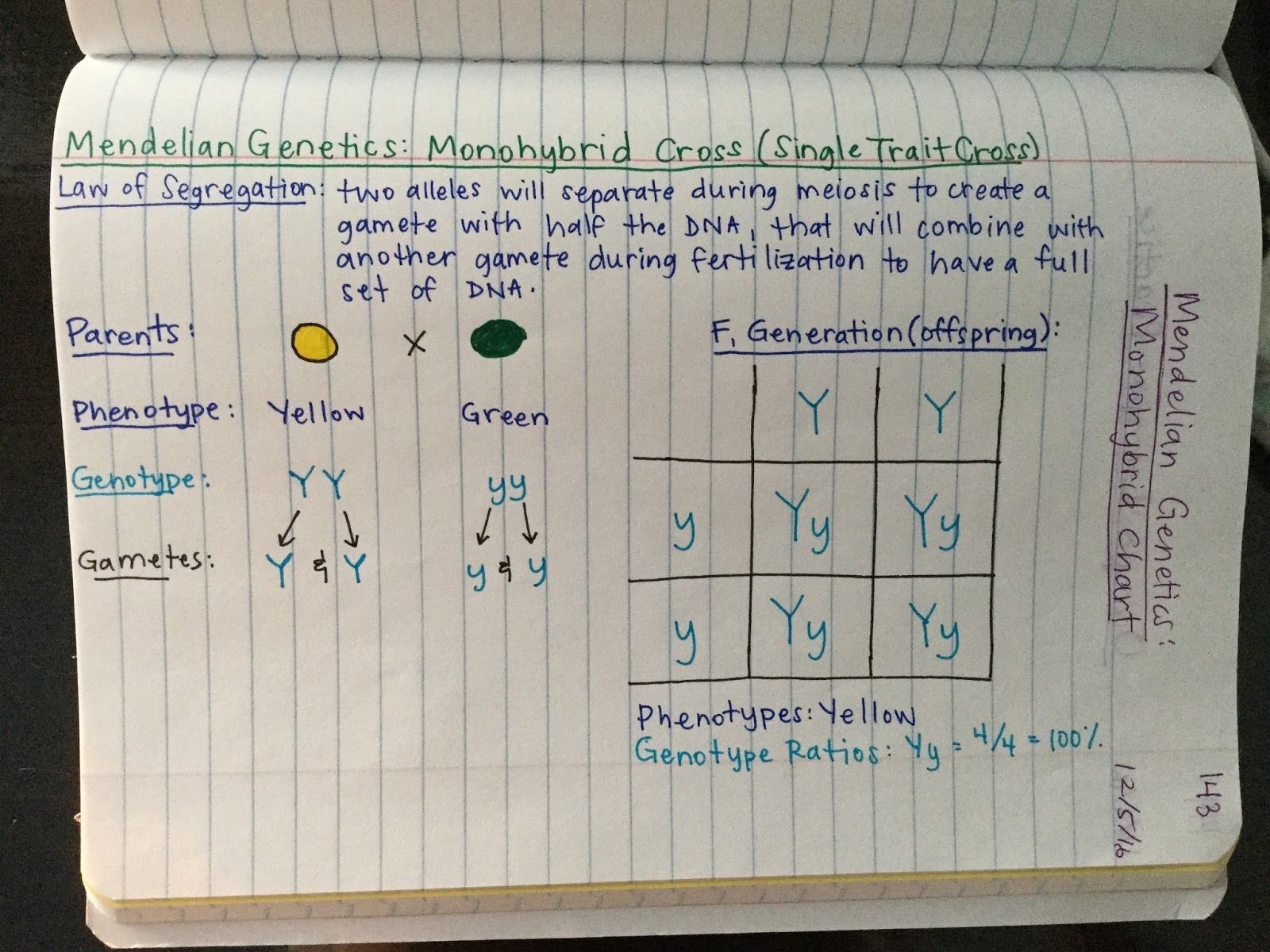
Example: Crossing two heterozygous plants (Pp x Pp).
Set up the Punnett square. Put one parent's alleles across the top. Put the other parent's alleles down the side.
Fill in each box with the combined alleles.
The possible genotypes are PP, Pp, and pp.
The resulting phenotypic ratio is 3 purple to 1 white.
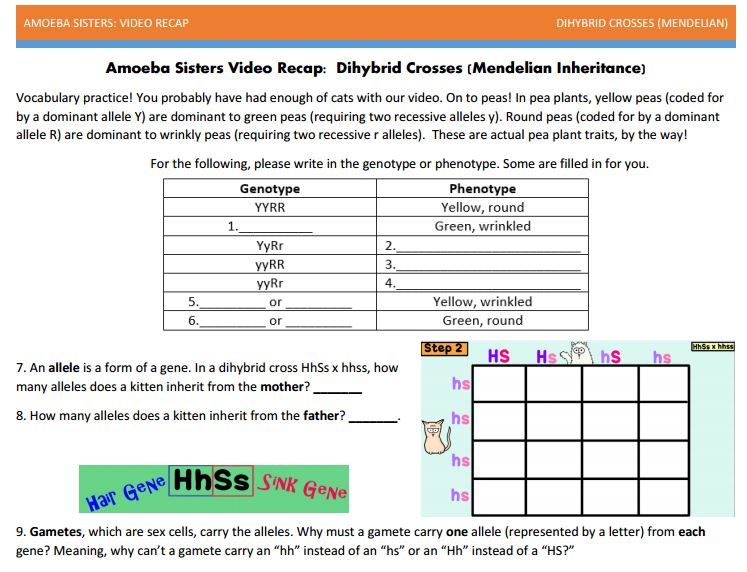
Amoeba Sisters Worksheet: Example Problem
The Amoeba Sisters offer helpful visuals. They break down complex topics.
One common example is coat color in mice. Brown (B) is dominant over white (b).
Problem: Cross a homozygous brown mouse (BB) with a homozygous white mouse (bb).
The genotypes of the parents are BB and bb.
The brown mouse can only produce gametes with the B allele.
The white mouse can only produce gametes with the b allele.
The Punnett square is simple in this case.
All offspring have the genotype Bb.
All offspring will have brown fur because brown (B) is dominant.
The genotypic ratio is 100% Bb.
The phenotypic ratio is 100% brown.
Another Example: Heterozygous Cross
Problem: Cross two heterozygous brown mice (Bb x Bb).
Each parent can produce gametes with either the B or the b allele.
Set up the Punnett square. B and b go across the top. B and b go down the side.
The possible genotypes are BB, Bb, and bb.
BB represents homozygous dominant (brown fur).
Bb represents heterozygous (brown fur).
bb represents homozygous recessive (white fur).
The genotypic ratio is 1 BB : 2 Bb : 1 bb.
The phenotypic ratio is 3 brown : 1 white.
Interpreting Results
Punnett squares show probabilities, not guarantees.
A large number of offspring increases accuracy. Genetic ratios are more likely to approach expected values in large populations.
Monohybrid crosses are a foundation. They're a gateway to more complex genetics.
Beyond Basic Problems
Some traits aren't strictly dominant or recessive. Incomplete dominance and codominance are exceptions.
Incomplete dominance blends traits. Red flower + white flower = pink flower.
Codominance shows both traits. Black feathers + white feathers = black and white speckled feathers.
Monohybrid crosses can be adapted. They can accommodate these non-Mendelian inheritance patterns.
Importance of Monohybrid Crosses
Understanding monohybrid crosses is crucial. It's a foundation for genetics.
They can be applied in agriculture. We can predict traits in crops and livestock.
They are also used in medicine. We can assess the risk of inheriting genetic disorders.
By using tools like Punnett squares, we can map out genetic traits and probabilities.
Monohybrid crosses are a simple yet powerful tool.